You create a single database in Azure SQL Database using either the Azure portal, a PowerShell script, or an Azure CLI script. You then query the database using Query editor in the Azure portal.
Prerequisite
- An active Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a free account.
Create a single database
This quickstart creates a single database in the serverless compute tier.
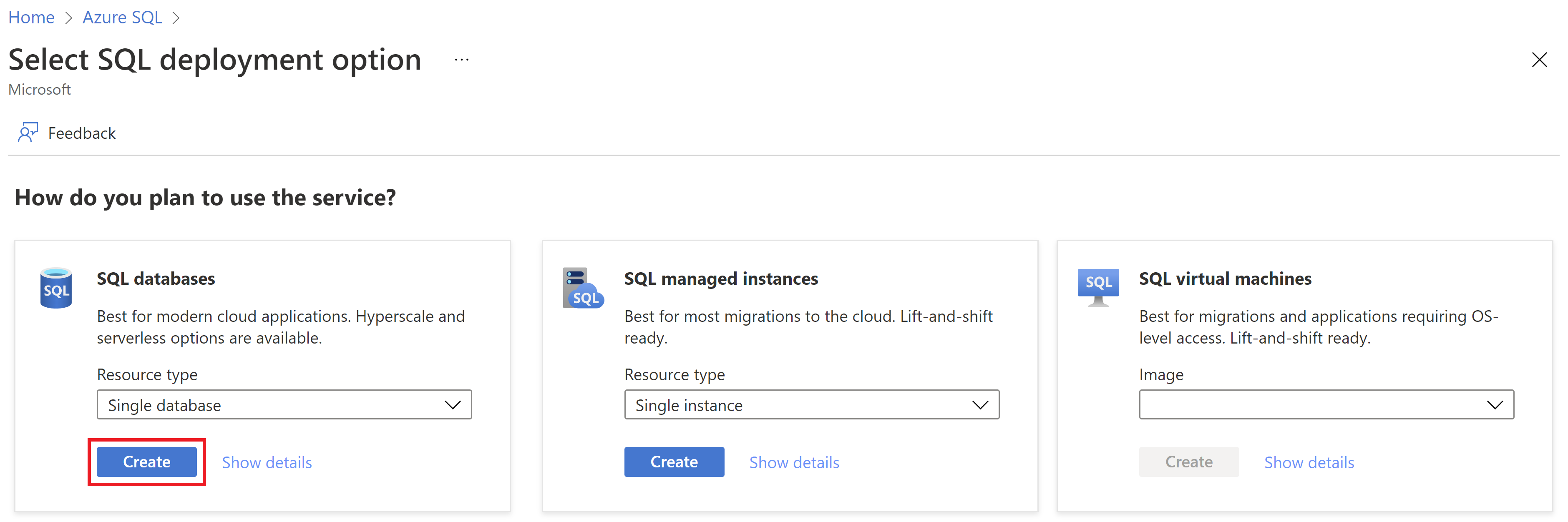
To create a single database in the Azure portal this quickstart starts at the Azure SQL page.
Browse to the Select SQL Deployment option page.
Under SQL databases, leave Resource type set to Single database, and select Create.
On the Basics tab of the Create SQL Database form, under Project details, select the desired Azure Subscription.
For Resource group, select Create new, enter myResourceGroup, and select OK.
For Database name enter mySampleDatabase.
For Server, select Create new, and fill out the New server form with the following values:
- Server name: Enter mysqlserver, and add some characters for uniqueness. We can't provide an exact server name to use because server names must be globally unique for all servers in Azure, not just unique within a subscription. So enter something like mysqlserver12345, and the portal lets you know if it is available or not.
- Server admin login: Enter azureuser.
- Password: Enter a password that meets requirements, and enter it again in the Confirm password field.
- Location: Select a location from the dropdown list.
Select OK.
Leave Want to use SQL elastic pool set to No.
Under Compute + storage, select Configure database.
This quickstart uses a serverless database, so select Serverless, and then select Apply.

Select Next: Networking at the bottom of the page.

On the Networking tab, for Connectivity method, select Public endpoint.
For Firewall rules, set Add current client IP address to Yes. Leave Allow Azure services and resources to access this server set to No.
Select Next: Additional settings at the bottom of the page.

On the Additional settings tab, in the Data source section, for Use existing data, select Sample. This creates an AdventureWorksLT sample database so there's some tables and data to query and experiment with, as opposed to an empty blank database.
Select Review + create at the bottom of the page:

On the Review + create page, after reviewing, select Create.
Query the database
Once your database is created, you can use the Query editor (preview) in the Azure portal to connect to the database and query data.
In the portal, search for and select SQL databases, and then select your database from the list.
On the page for your database, select Query editor (preview) in the left menu.
Enter your server admin login information, and select OK.

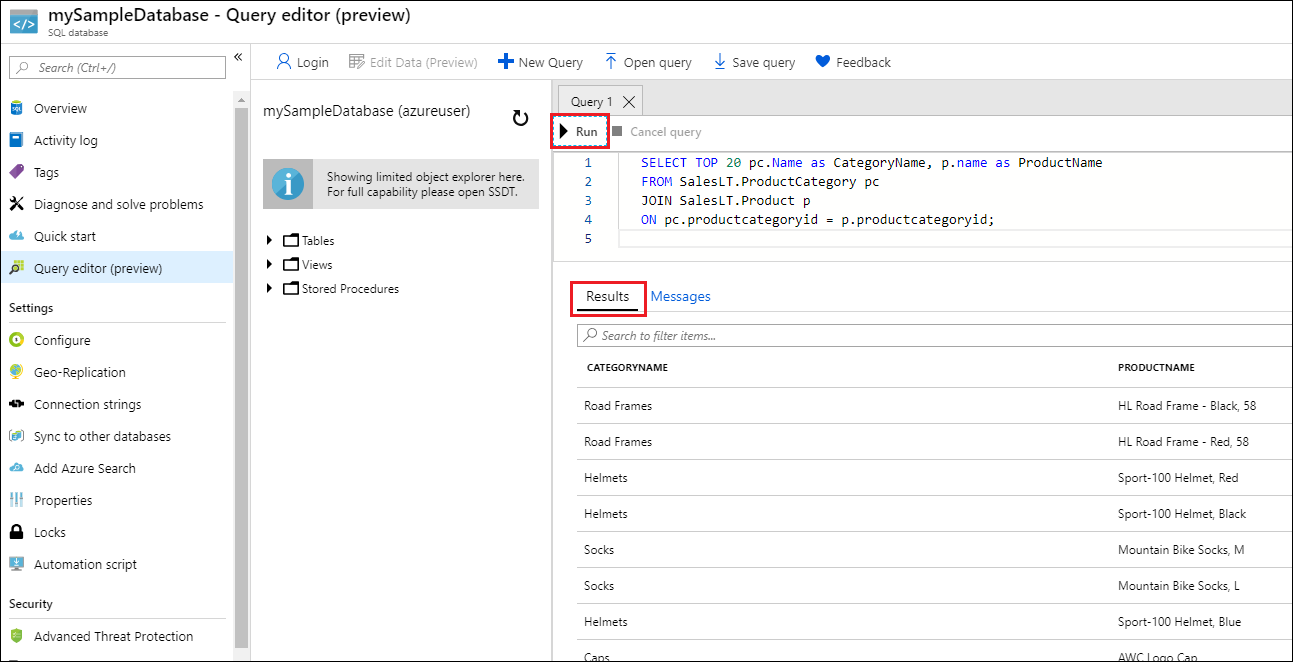
Enter the following query in the Query editor pane.
SQLSELECT TOP 20 pc.Name as CategoryName, p.name as ProductName FROM SalesLT.ProductCategory pc JOIN SalesLT.Product p ON pc.productcategoryid = p.productcategoryid;Select Run, and then review the query results in the Results pane.
Close the Query editor page, and select OK when prompted to discard your unsaved edits.
Clean up resources
Keep the resource group, server, and single database to go on to the next steps, and learn how to connect and query your database with different methods.
When you're finished using these resources, you can delete the resource group you created, which will also delete the server and single database within it.
To delete myResourceGroup and all its resources using the Azure portal:
- In the portal, search for and select Resource groups, and then select myResourceGroup from the list.
- On the resource group page, select Delete resource group.
- Under Type the resource group name, enter myResourceGroup, and then select Delete.


0 Comments