Group Policy Preferences (GPP) first came in with Server 2008 and were enhanced for Server 2008 R2, To be able to apply them to older Windows clients, you need to install the “Client side Extensions” (CSE), You can either script this, deploy with a group policy, or if you have WSUS you can send out the update that way.
| OS Download LinkClient side extensions for Windows XP (x86) link Client side extensions for Windows XP (x64) link Client side extensions for Windows Vista (x86) link Client side extensions for Windows Vista (x64) link Client side extensions for Windows Server 2003 (x86) link Client side extensions for Windows Server 2003 (x64) link Client side extensions for Windows 7 (x86) Already Installed Client side extensions for Windows 7 (x64) Already Installed Client side extensions for Windows 8 (x64) Already Installed |
Solution
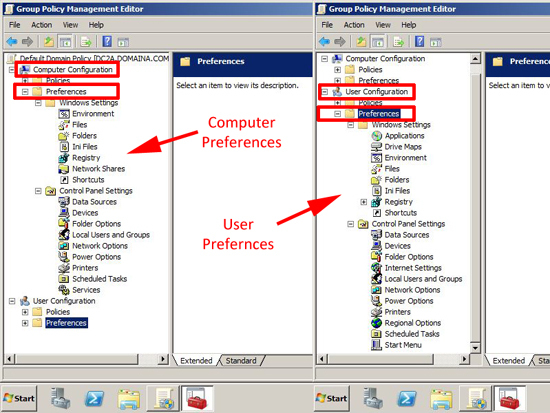
You may not have noticed, but if you edit or create a group policy after Server 2008 now, you will see there is a “Preferences” branch. Most IT Pro’s will have seen the addition of the “Policies” folder some time ago because it adds an extra level to get to the policies that were there before 🙂
OK Cool! What can you do with them?
1. Computer Preferences: Windows Settings
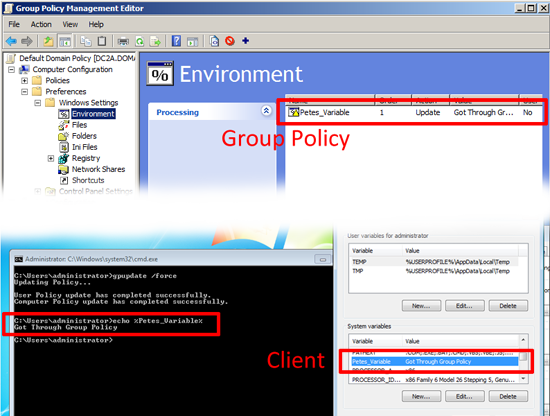
Environment: Lets you control, and send out Environment variables via Group Policy.
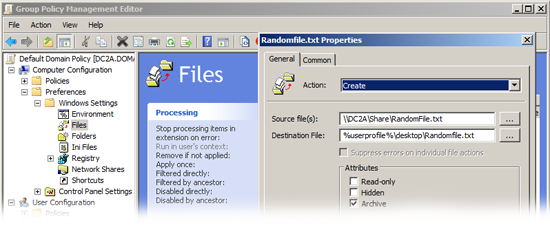
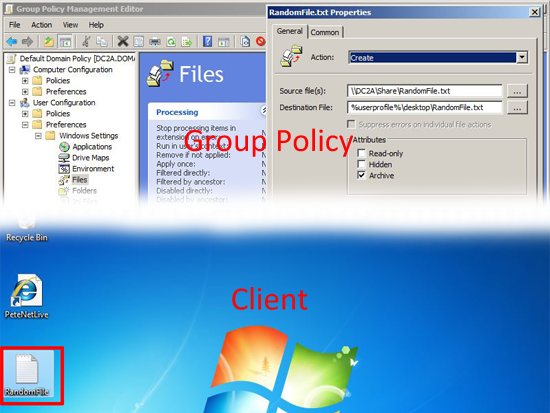
Files: Allows you to copy, modify the attributes, replace or delete a file (for folders see the next section).
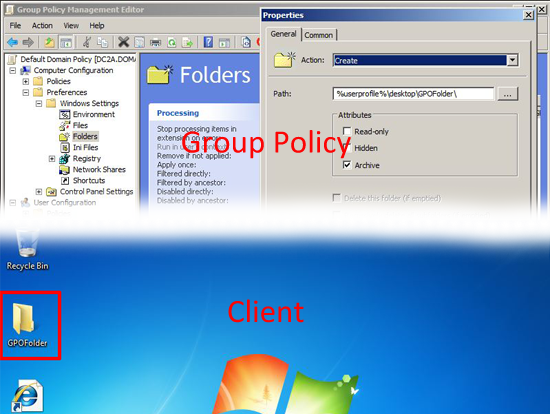
Folder: As above, but for folders.
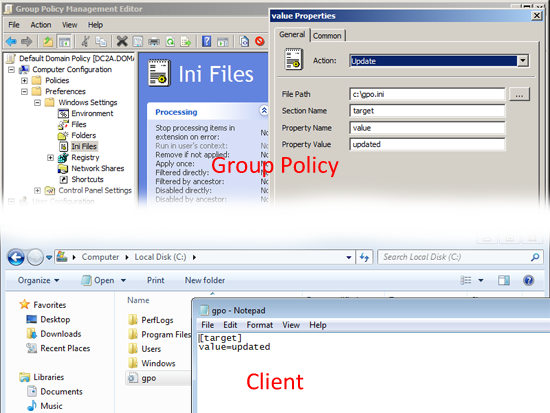
Ini Files: Allows you to Create, Replace, Update or Delete an ini file.
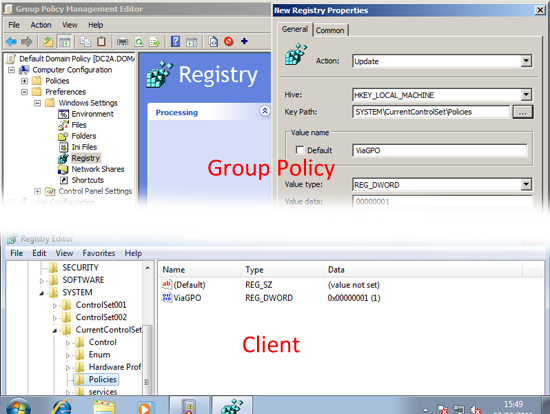
Registry: Allows you to Create, Replace, Update or Delete a Registry value, You can either manually type in the reference use a Wizard, or extract the key(s) values you want to send them out via group policy.
Network Shares: Allow you to Create, Replace, Update, or Delete shares on clients via group policy.
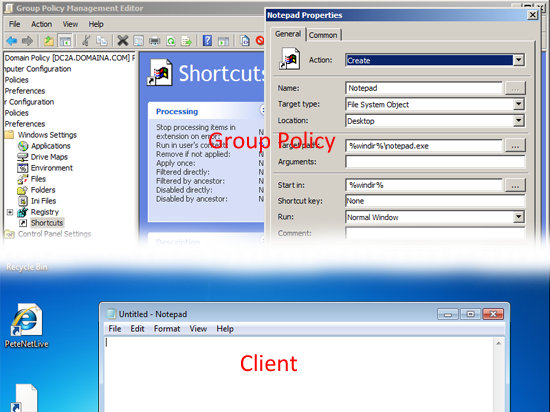
Shortcuts: Allows you to Create, Replace, Update, or Delete shortcuts on clients via group policy.
2. Computer Preferences: Control Panel Settings
Data Sources: Allows you to Create, Replace, Update, or Delete, Data Sources and ODBC settings via group policy. (Note: there’s a bug if your using SQL authentication see here).
Devices: Lets you enable and disable hardware devices by type and class, to be honest it’s a little “clunky”.
Folder Options: Allows you to set “File Associations” and set the default programs that will open particular file extensions.
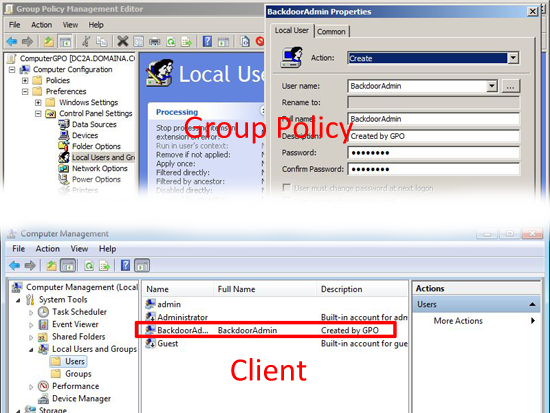
Local Users and Groups: Lets you Create, Replace, Update, or Delete either local users OR local groups. Handy if you want to create an additional admin account, or reset all the local administrators passwords via group policy.
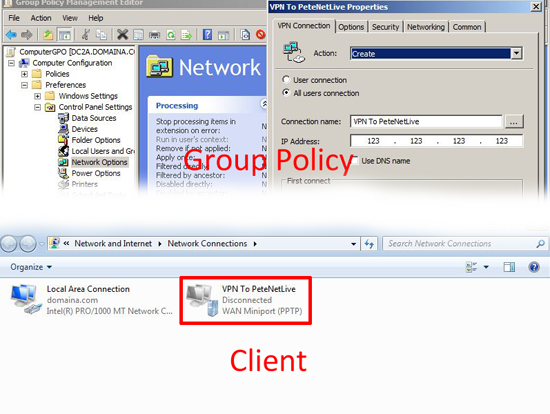
Network Options: Lets you send out VPN and dial up connection settings to your clients, handy if you use PPTP Windows Server VPN’s.
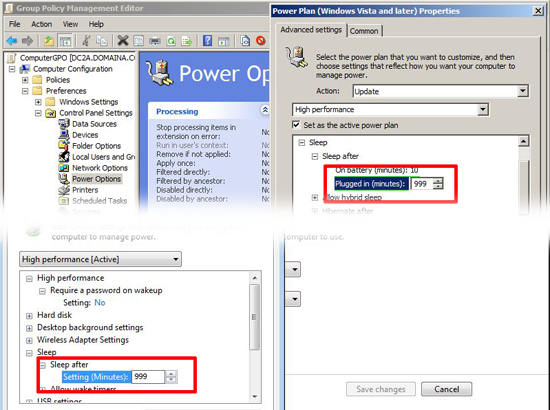
Power Options: With XP these are Power Options and Power Schemes, With Vista and later OS’s they are Power Plans. This is much needed, I’ve seen many “Is there a group policy for power options?” or disabling hibernation questions in forums. And you can use the options Tab, to target particular machine types (i.e. only apply if there is a battery present).
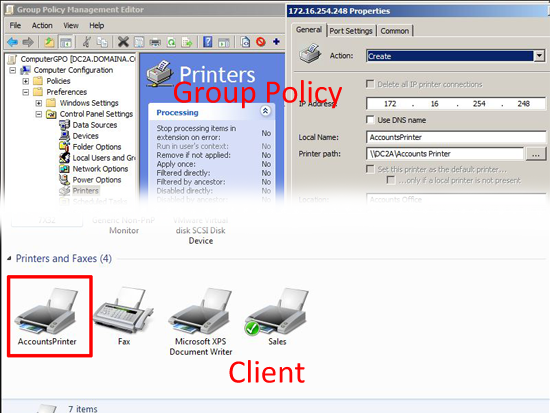
Printers: Lets you install printers (local or TCP/IP), handy if you want all the machines in accounts to have the accounts printer. for further info see,
Deploying Printers with Group Policy Preferences
Scheduled Tasks: Lets you create a scheduled task or an immediate task (Vista or Later), this could be handy to deploy a patch or some virus/malware removal process.
Service: Essentially anything you can do in the services snap in you can push out through group policy, set services to disables or change the logon credentials used for a service. In addition you can set the recovery option should a service fail.
3. User Configuration: Windows Settings
Applications: I can’t work out what these are for!
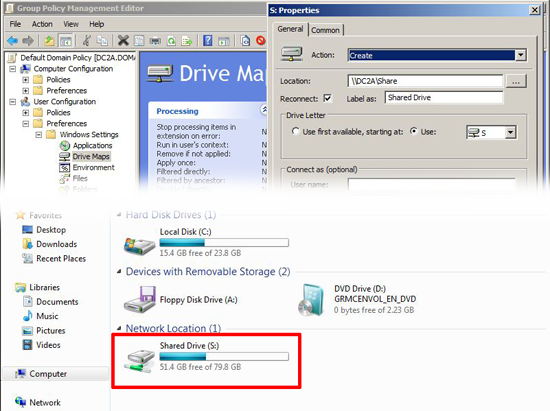
Drive Mappings: Traditionally done by login script or from the user object, but use this and you can assign mapped drives on a user/group basis.
Environment: As above lets you control and send out Environment variables via Group Policy, but on a user basis.
Files: As above. allows you to copy, modify the attributes, replace or delete a file (for folders see the next section), but on a user basis.
Folders: As above, but for folders on a user by user basis.
Ini Files: As above, allows you to Create, Replace, Update or Delete an ini file, on a user by user basis.
Registry: As above, allows you to Create, Replace, Update or Delete a Registry value, You can either manually type in the reference use a Wizard, or extract the key(s) values you want to send out via group policy, this time for users not computers.
Shortcuts: As Above, allows you to Create, Replace, Update, or Delete shortcuts on clients via group policy for users.
4. User Configuration: Control Panel Settings
All of the following options are covered above on “Computer Configuration”
Data Sources Devices Folder Options Local Users and Groups Network Options Power Options Printers Scheduled Tasks
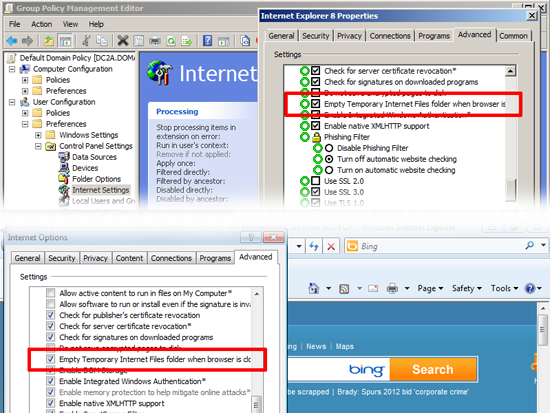
Internet Settings: Using this Group Policy you can specify Internet Explorer settings/options on a user by user basis.
Regional Options: Designed so you can change a users Locale, handy if you have one user who wants an American keyboard.
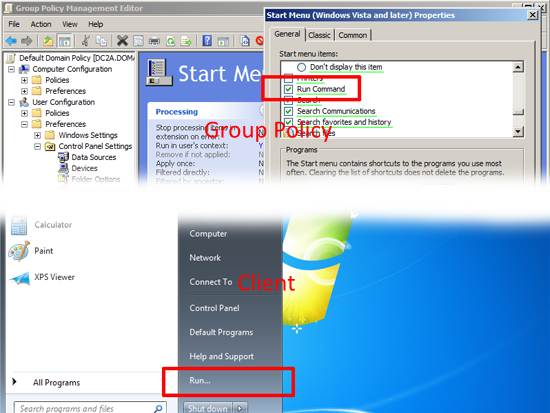
Start Menu: Provides the same functionality as right clicking your task bar > properties > Start Menu > Customise, only set user by user.


0 Comments